How to Choose the Right Airplane Wire for Your Aviation Needs
Choosing the right airplane wire is crucial for ensuring safety and performance in aviation applications. As noted by aviation expert John Smith, "The integrity of an aircraft's electrical system heavily relies on the quality and suitability of the airplane wire used." The selection process involves understanding various factors, such as wire types, materials, and specific aviation standards. Understanding these nuances can significantly impact the reliability of the aircraft's systems.
In the aviation industry, the importance of airplane wire cannot be overstated. It serves as the backbone of the electrical systems that power everything from navigational instruments to communication devices. With a wide range of options available, it's essential for professionals in the field to make informed decisions. John Smith emphasizes the importance of thorough research and adherence to industry regulations when selecting airplane wire, stating that "a well-informed choice not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures compliance with safety standards."
As we delve into the intricacies of choosing the right airplane wire, we will explore key considerations, including wire gauge, insulation types, and environmental factors. By understanding these aspects, aviation professionals can make choices that enhance aircraft performance and safety while meeting the rigorous demands of the industry.
Understanding Different Types of Airplane Wires in Aviation
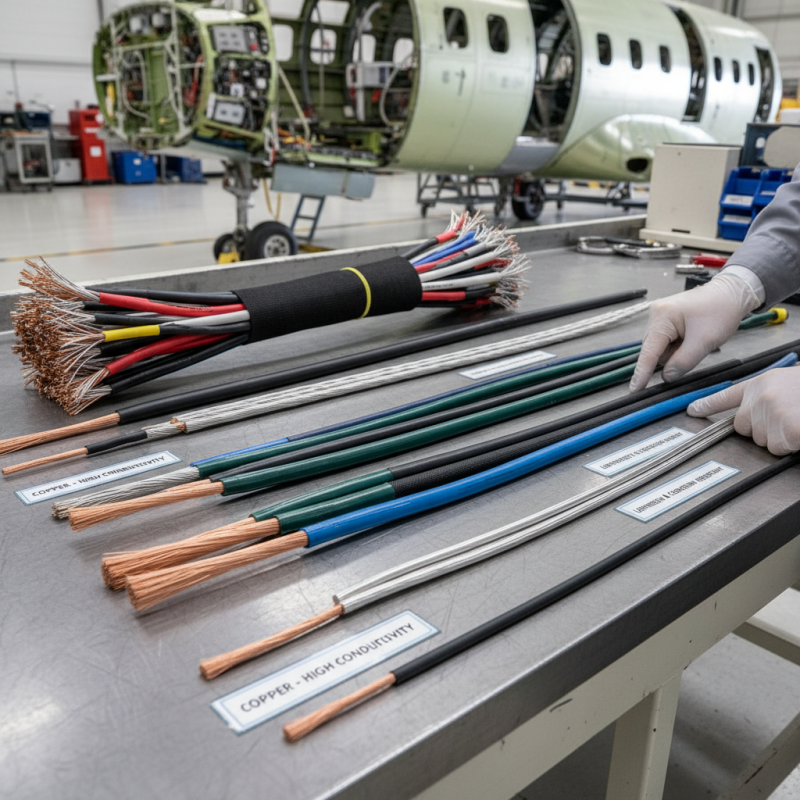
When it comes to aviation, selecting the appropriate airplane wire can greatly impact both safety and efficiency. There are several types of wires commonly used in aircraft systems, each designed to meet specific requirements. One prevalent type is the copper wire, favored for its excellent conductivity and flexibility. Copper wires are often found in various systems, such as power distribution and control applications. However, due to their susceptibility to corrosion, wires often need proper insulation to enhance durability in the harsh aviation environment.
Another key type is the aluminum wire, which is lighter than copper and can offer significant weight savings in certain applications. Aluminum wires are particularly useful in high-voltage applications, where weight reduction is crucial for overall aircraft performance. However, while aluminum possesses good conductivity, it is not as conductive as copper, which may necessitate using a larger diameter wire to achieve the same performance standards. Additionally, proper connections and termination methods are essential to mitigate issues related to corrosion and mechanical fatigue in aluminum wiring systems.
In recent years, advancements in technology have introduced the use of composite materials in airplane wiring. These composites can provide enhanced resistance to environmental factors while maintaining a lightweight profile. Moreover, advancements in insulation materials have led to wires that can better withstand extreme temperatures and oil exposure, further improving reliability in flight operations. Understanding the distinct characteristics of each wire type allows aviation professionals to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational requirements.
Airplane Wire Types and Their Applications
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Airplane Wire

When selecting airplane wire, several key factors come into play to ensure optimal performance and safety in aviation applications. First and foremost, it is essential to consider the wire's material composition. Common materials include copper and aluminum, each offering distinct advantages such as weight reduction and conductivity. Copper, while heavier, provides superior conductivity, making it a preferred choice for critical electrical systems. In contrast, aluminum wire is lighter and more corrosion-resistant, which can be advantageous in various airborne environments.
Next, assessing the wire's insulation type is crucial. Insulation serves as a protective barrier against environmental factors and electrical interference. Various insulation materials, including PVC, Teflon, and silicone, cater to specific temperature ranges and chemical resistances. For instance, Teflon insulation is known for its high-temperature tolerance, making it suitable for areas exposed to extreme conditions. Selecting the right insulation not only enhances durability but also minimizes the risk of electrical faults.
Lastly, the gauge of the wire should align with the aircraft’s electrical requirements. Thicker wire (lower gauge number) can carry more current, making it essential for high-load applications. Conversely, thinner wire (higher gauge number) is suitable for low-power circuits. Understanding the specific needs of the aircraft, including voltage and current specifications, will facilitate informed decisions that contribute to the overall safety and effectiveness of the aviation system.
Evaluating Wire Specifications for Safety and Performance
When selecting the right airplane wire for your aviation needs, evaluating wire specifications is crucial for ensuring both safety and performance. Various factors such as voltage rating, current-carrying capacity, and environmental resistance play significant roles in determining the suitability of wire for specific applications. Wires must be able to withstand extreme temperatures and resist corrosion, as they often operate in harsh conditions found in aviation environments.
Tips for choosing the right wire include first understanding the specific requirements of your aircraft system. Take into account factors like the wire’s insulation type, which can affect its performance and durability. Additionally, ensure that the wire complies with relevant aviation standards; this guarantees that it meets safety regulations essential for aviation applications.
Another important consideration is the weight of the wire. The aviation industry prioritizes lightweight components, as excess weight can negatively affect performance and fuel efficiency. Opt for wires that provide a balance between durability and weight, as this aspect impacts the overall efficiency of the aircraft. Always consult technical specifications and experts in the field to make informed decisions that align with your aviation requirements.
Common Applications of Airplane Wire in Various Aircraft Types
Airplane wire plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and functionality of various aircraft types. In commercial aviation, for instance, many aircraft utilize copper or aluminum alloy wires that provide excellent conductivity and lightweight properties. These wires are integral to the aircraft's electrical systems, which power everything from navigation and communication to lighting and flight control systems. The extensive use of these wires helps maintain efficiency while minimizing weight, a critical factor in aerodynamics and fuel consumption.
In general aviation, the needs can vary significantly depending on the specific type of aircraft. Light sport aircraft often employ simpler wiring systems, typically using smaller gauge wire that is both cost-effective and easy to install. On the other hand, larger business jets may require more robust wiring solutions that can handle higher current loads and provide redundancy for critical systems. This often means using multi-stranded wires that enhance flexibility and durability while resisting vibrations and environmental challenges. Understanding these common applications enables aviation professionals to select the right type of airplane wire that aligns with the unique operational demands of different aircraft.
Best Practices for Maintaining and Inspecting Airplane Wire
Maintaining and inspecting airplane wire is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of aviation operations. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Technicians should use standardized checklists to ensure thorough evaluation, focusing on the wire’s insulation integrity, physical condition, and overall connectivity. Visual inspections can often reveal issues like fraying or discoloration, but more advanced diagnostic tools, such as multimeters, can help assess the wire’s electrical properties, ensuring they meet operational standards.
Best practices also involve adhering to proper storage and installation protocols to extend the lifespan of airplane wire. Wires should be stored in a clean, dry environment to avoid moisture-related damage. Additionally, during installation, it is important to avoid sharp bends and ensure proper securing to minimize movement that could lead to wear over time. Implementing routine maintenance schedules and documenting inspection findings will help track the condition of the wire and address any potential problems before they compromise flight safety. Regular training and updates for personnel involved in these processes will further enhance the effectiveness of wire maintenance and inspection practices.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Essentials of Cable Harness: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
-

Top 10 Best Control Wire Types for Optimal Performance and Durability
-

Top 10 Must-Know Facts About Cable Harnesses for Your Next Project
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Perfect Cable Harness for Your Project
-

Top 10 Power Wire Types You Need for Your Electrical Projects in 2023
-

Top 10 Cable Wire Cable Types for Your Home and Business Needs
